Pression artérielle : comprendre vos relevés
Peer reviewed by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGPLast updated by Victoria RawLast updated 4 Sept 2025
- TéléchargerTélécharger
- Partager
Selon la British Heart Foundation (BHF), environ 3 personnes sur 10 au Royaume-Uni souffrent d'hypertension artérielle. L'hypertension artérielle passe souvent inaperçue, ce qui fait que 5 millions d'adultes au Royaume-Uni ignorent qu'ils en souffrent. Contrôler régulièrement sa tension artérielle et comprendre ses résultats est essentiel pour un diagnostic et un traitement précoces.
Sponsorisé
Fondation britannique du cœur
Ce dossier est parrainé par la British Heart Foundation, le principal bailleur de fonds de la recherche sur les maladies cardiaques et circulatoires en Europe.
Le contenu suit la politique éditoriale du Patient.

Dans cet article :
Poursuivre la lecture ci-dessous
What is blood pressure?
Your blood pressure is the force at which your blood pushes against the walls of your arteries as it's pumped around your body.
If your blood pressure is too low (hypotension), it can cause you to feel dizzy or even faint.
If your blood pressure is too high (hypertension), it can increase your chance of heart failure, heart attack, or stroke.
Quelles sont les causes de l'hypertension artérielle ?
In most cases, there isn't a specific reason for the cause of high blood pressure, but most people develop it because of their diet, lifestyle or medical condition.
Your likelihood of developing high blood pressure increases as you age, but also if you:
Have someone in your family with high blood pressure.
Are someone who smokes.
Drink too much alcohol.
Eat too much salt and not enough fruit and vegetables.
Don't get enough exercise.
Are overweight or living with obesity.
High blood pressure is more common in deprived areas, and rates are higher in people who are of black African or black Caribbean descent. Changes in your diet and increasing activity levels can often help improve your blood pressure.
Poursuivre la lecture ci-dessous
Can pregnancy lead to high blood pressure?
If you're pregnant, your blood pressure may rise - especially if you have a history of the condition.
During pregnancy, two types of high blood pressure can develop.
Gestational hypertension: This is high blood pressure that starts in pregnancy and returns to normal after your baby is born.
Pre-eclampsia: This is a more severe type of high blood pressure that can develop in some women - typically after 20 weeks of pregnancy. If not managed properly, it can harm the mother's organs and cause significant health complications. This is a medical emergency and you need to see a health professional straight away if you have any of the symptoms of pre-eclampsia.
Symptoms of pre-eclampsia are:
Changes in vision - such as blurred vision, seeing spots, flashes or sensitivity to light.
Maux de tête sévères.
Swelling of your face, hands or feet.
Trouble breathing.
Pain above your tummy, just under your ribs.
New severe nausea and vomiting.
If you develop high blood pressure while pregnant, a midwife specialising in pregnancy-related hypertension will evaluate your condition in a hospital.
If you're pregnant with a history of high blood pressure, see a specialist to discuss treatment. If you're on blood pressure medicine and planning a pregnancy, talk to your doctor to possibly switch treatment.
If you're already pregnant, tell your doctor immediately, as some medicines may be unsafe during pregnancy.
Checking your blood pressure
You can ask your doctor for a blood pressure check. If you're aged 40 to 74 in England, you're eligible for a blood pressure check as part of the free NHS Health Check, offered every five years.
You can get your blood pressure tested at several places for free - such as your local pharmacy, or your registered medical practice. You can also take it at home with your own blood pressure monitor.
If you are buying a blood pressure monitor to use at home, choose one that has been accredited by the British and Irish Hypertension Society (BIHS). This means your monitor has been tested to ensure its accuracy. For a list of validated blood pressure monitors, visit the BIHS website.
Monitors usually cost around £20 - £100. You can buy BHIS-accredited blood pressure monitors directly from the BHF. What’s more, the profits go directly towards funding the BHF's lifesaving research.
If your blood pressure is usually healthy, check it every 6 months or so using an approved home monitor.
Poursuivre la lecture ci-dessous
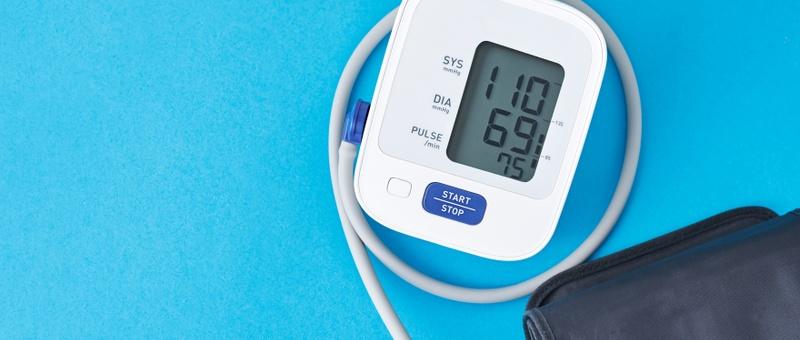
How to read your blood pressure numbers
Blood pressure machines usually include an arm cuff to measure your blood pressure. This is wrapped around your upper arm and inflated until tight - automatic devices use sensors in the cuff to display results digitally. A healthcare professional may also use a stethoscope.
Your blood pressure reading is measured in millimetres of mercury (mmHg) and recorded as two numbers:
Systolic pressure - the top number in a blood pressure reading. It measures the pressure of blood against your artery walls as your heart pumps it around your body.
Diastolic pressure - the bottom number in a blood pressure reading. It measures the pressure of blood in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
A typical blood pressure reading will be displayed with the top number always above the bottom.
A healthy blood pressure reading is typically between 90/60 - 120/80 mmHg.
A high blood pressure reading is consistently above 140/90 mmHg - or 135/85 if taken at home.
A blood pressure reading consistently between 120/80 - 139/89 mmHg is generally considered OK. However, it could suggest an increase in your chances of developing high blood pressure.
The stress you may feel when you have your blood pressure measured by a healthcare professional in an unusual setting - commonly called white coat syndrome - may mean your figures are inaccurate or too high. Your healthcare professional may recheck it or ask you to check it yourself at home. They may also use an ambulatory blood pressure monitor (ABPM) which tracks your blood pressure over a 24-hour period.
Measuring your blood pressure at home
When you measure your blood pressure at home, there are some things you should do to help get a more accurate reading.
Il s'agit notamment de
Try not to eat, exercise, or take medicines beforehand - avoid caffeine and smoking for 30 minutes before your reading.
Find a quiet space to sit for 5 minutes before checking - make sure you're sitting upright, with both feet flat on the ground and your arm resting comfortably at chest height.
Be still and silent while measuring your blood pressure.
Measure your blood pressure at the same time every day - each time, take three readings 1-2 minutes apart.
High blood pressure is categorised into 3 stages:
Stage 1: When your blood pressure is between 140/90 - 159/99 mmHg at the doctor's, or 135/85 - 149/94 mmHg at home.
Stage 2: When your blood pressure is between 160/100 - 180/120 mmHg at the doctor's, or above 150/95 mmHg at home.
Stage 3: When your systolic blood pressure is over 180 mmHg, or your diastolic blood pressure is over 120 mmHg at the doctor's.
The NHS offers a simple tool to help you understand your blood pressure reading.
This last stage - called severe hypertension with a blood pressure reading of 180/120 or higher - requires immediate medical attention. Go to your nearest emergency department.
Simpler ways to help lower your high blood pressure
There are many straightforward lifestyle changes you can make to help lower your blood pressure - and keep it lower. These lifestyle changes will support any medicines you are taking and improve your overall health.
Eat healthily: Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables - go for five a day - whole grains, and low-fat dairy. Choose foods low in cholesterol, saturated fat, and salt.
Drink less alcohol: Keep your weekly alcohol within safer limits.
Lower your caffeine intake: Have less coffee, tea, and fizzy drinks.
Lose weight: Especially if you're carrying extra weight around your waist. Aim to get your weight within a healthy BMI range.
Exercise regularly: Try to have at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week - for at least ten minutes a day. Find activities that you enjoy so you are more likely to keep on doing them.
Avoid stress: Do more of the things you enjoy and less of the things that trigger your stress.
Sleep well: Get at least 7 hours a day.
Don't smoke: Stopping smoking is one of the best things you can do for your blood pressure and your overall health.
Blood pressure medicine
Your doctor may prescribe a course of treatment for high blood pressure if your readings are high at the surgery, high from your home readings, or if lifestyle changes haven't been able to lower your blood pressure if you were borderline.
The type and amount of medicines prescribed for you will be down to several factors such as how high your blood pressure is and your age.
If you have any questions or concerns about high blood pressure, heart disease or circulatory conditions, speak to your doctor or contact the BHF's Heart Helpline. Experienced cardiac nurses are available to assist you with a range of support topics. You can reach out to them by phone, email, or virtual chat.
Sélection de patients pour L'hypertension artérielle

Santé générale et mode de vie
Les protéines d'origine végétale pourraient contribuer à prévenir l'hypertension artérielle
Eating a greater amount of minimally processed plant-based proteins - such as beans, nuts and lentils - may lower your chance of developing high blood pressure, according to new research.
by Laura Williamson

Santé cardiaque et vaisseaux sanguins
Enregistrement de la pression artérielle à domicile et en ambulatoire
La prise de la tension artérielle en dehors du cabinet médical est recommandée pour la plupart des personnes suspectées d'hypertension artérielle. En effet, les mesures effectuées au cours de la vie quotidienne sont plus précises que celles effectuées dans un cabinet médical. Elles peuvent également être utilisées pour donner au médecin des informations sur l'efficacité d'un médicament contre l'hypertension. La méthode idéale est la surveillance ambulatoire de la tension artérielle, qui utilise un enregistreur portable. Si cette méthode n'est pas pratique ou inconfortable, les mesures peuvent être effectuées à domicile à l'aide d'un appareil de mesure de la tension artérielle traditionnel.
par le Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGP
Historique de l'article
Les informations contenues dans cette page ont été évaluées par des cliniciens qualifiés.
Date de la prochaine révision : 4 septembre 2028
4 Sept 2025 | Dernière version
7 Oct 2024 | Publié à l'origine
Auteur: :
Victoria Raw

Demandez, partagez, connectez-vous.
Parcourez les discussions, posez des questions et partagez vos expériences sur des centaines de sujets liés à la santé.

Vous ne vous sentez pas bien ?
Évaluez gratuitement vos symptômes en ligne